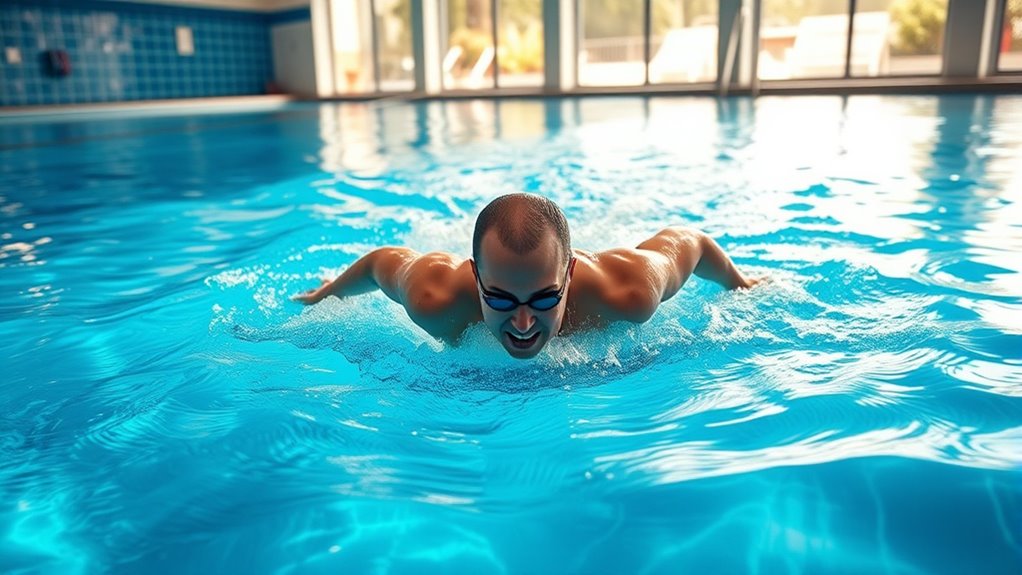
Lap swimming tones your muscles by engaging your entire body in low-impact resistance, which boosts endurance and builds lean muscle mass. It’s gentle on your joints while providing a full-body workout that improves strength, flexibility, and stability. Swimming also burns calories effectively and supports weight management. Plus, you can customize your routine to match your fitness level. Keep exploring to uncover more ways swimming helps you achieve your fitness goals.
Key Takeaways
- Water resistance provides full-body muscle engagement, promoting lean muscle development and toning across arms, shoulders, core, and legs.
- The low-impact, joint-friendly nature of swimming reduces stress on cartilage while enhancing muscle strength and endurance.
- Continuous resistance challenges muscles, leading to balanced muscle toning and improved overall body composition.
- Swimming’s dynamic strokes and resistance build muscle definition without high-impact stress, resulting in a toned physique.
- Regular lap swimming boosts metabolic rate and supports fat loss, revealing toned muscles over time.
Top picks for "swimm benefit swimmer"
Open Amazon search results for this keyword.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Full-Body Engagement for Toning Muscles

Because swimming involves multiple muscle groups simultaneously, it provides an effective full-body workout that tones your muscles. Water resistance plays a vital role, making every movement more challenging without added strain on your joints. As you propel yourself through the water, muscle activation occurs across your arms, shoulders, core, legs, and back. This constant resistance encourages your muscles to work harder, leading to improved strength and tone over time. Unlike workouts that target only specific areas, swimming engages your entire body, helping you develop balanced muscle mass. Plus, the fluid environment allows you to move freely and naturally, maximizing muscle engagement with less risk of injury. The full-body engagement involved in swimming also stimulates your cardiovascular system, enhancing overall health. Incorporating muscle activation techniques during your swim can further optimize your workout and results. Overall, swimming’s full-body engagement makes it a highly efficient way to tone muscles while enjoying the soothing properties of water.
Low-Impact Exercise Protects Joints
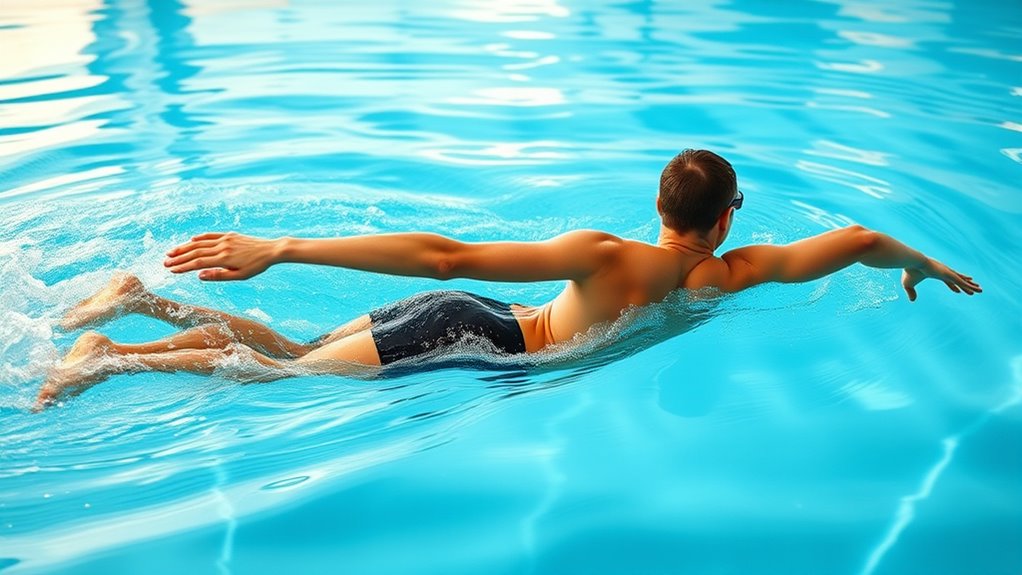

Swimming is gentle on your cartilage, helping to protect your joints from wear and tear. It reduces overall joint stress, making it an ideal exercise if you’re dealing with pain or inflammation. Plus, it supports rehab efforts by providing a safe way to stay active without risking further injury. Regular swimming can also promote joint health by increasing circulation and delivering essential nutrients to cartilage. Additionally, the low-impact nature of swimming minimizes the risk of injury that can occur with more intense or high-impact activities.
Gentle on Cartilage
Since it minimizes impact on your joints, lap swimming is an excellent low-impact exercise that helps protect cartilage. The buoyant nature of water reduces the pressure on your joints, allowing for effective movement without excessive stress. This gentle activity promotes cartilage preservation by decreasing the wear and tear that high-impact exercises can cause. Additionally, water provides natural joint cushioning, supporting smoother motion and reducing pain or discomfort. Because you’re not pounding your joints with repetitive impact, swimming minimizes the risk of joint deterioration over time. It also encourages proper body alignment, which can help prevent joint strain and improve overall movement efficiency. Engaging in aquatic exercise can also increase joint stability, further supporting long-term joint health, especially if you’re managing arthritis or recovering from injury. Overall, swimming offers a safe, effective way to stay active while safeguarding your cartilage and maintaining healthy joints.
Reduces Joint Stress
Engaging in lap swimming considerably reduces joint stress compared to high-impact activities. Water resistance provides gentle opposition, allowing you to move smoothly without jarring your joints. This low-impact environment minimizes wear and tear, making it ideal for joint preservation. Unlike running or jumping, swimming supports your body weight, decreasing the force exerted on your knees, hips, and ankles. The buoyant nature of water cushions your joints, reducing pain and inflammation. As you glide through the pool, you benefit from a full-body workout without the risk of overstressing your joints. This makes lap swimming especially suitable for those with arthritis or joint injuries, helping you stay active while protecting your joints from damage. Additionally, the well-draining soil used in pool landscaping can help prevent waterlogging and maintain a safe environment around your swimming area, which aligns with the importance of proper return policies for equipment and accessories used in your swim setup. Proper hydration during swimming sessions is also crucial to prevent muscle cramps and maintain overall health. Maintaining good water quality is essential to prevent infections and ensure a healthy swimming environment. Furthermore, selecting appropriate swimsuits can enhance comfort and reduce chafing during your aquatic activities.
Supports Rehab Efforts
Because low-impact exercise minimizes stress on your joints, lap swimming is an effective way to support rehab efforts. It’s often used in aquatic therapy to aid injury recovery by reducing strain while promoting movement. Swimming allows you to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility without risking further damage. This makes it ideal for those recovering from joint injuries or surgeries. Additionally, recognizing patterns in numbers can help you understand your body’s signals during recovery. Furthermore, understanding support hours and schedules can assist in planning consistent routines that optimize rehabilitation. Notably, the influence of Best Anime Movies on cultural narratives can motivate individuals to pursue holistic well-being through consistent activity. Incorporating sound therapy techniques like rhythmic auditory stimulation may further enhance recovery and engagement during rehabilitation sessions.
Enhances Cardiovascular Endurance
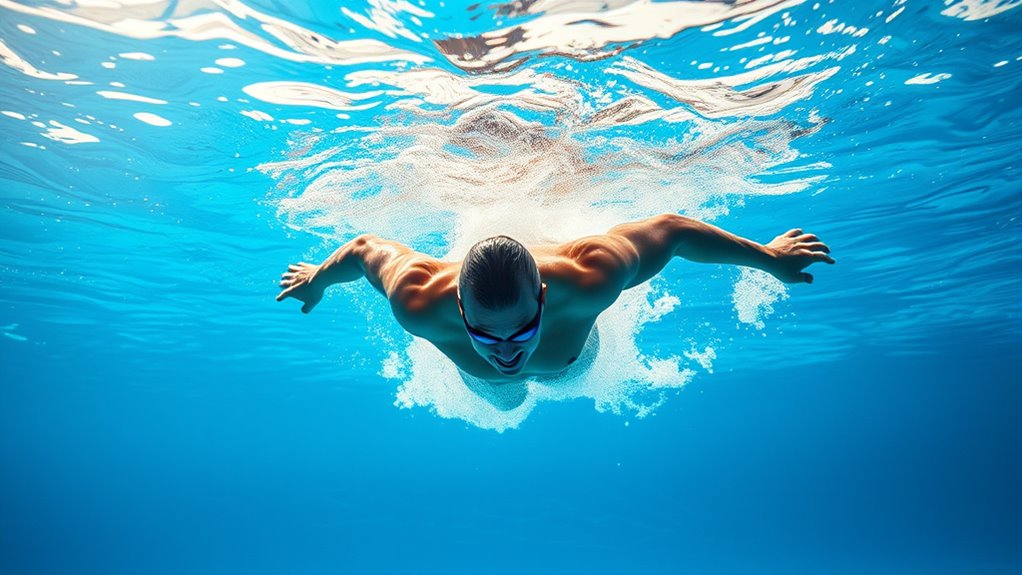

When you swim regularly, your heart becomes more efficient at pumping blood, helping you stay active longer. Your lungs also improve their capacity, making it easier to breathe during physical activities. Over time, consistent swimming builds your endurance, so you can sustain effort without fatigue. Additionally, engaging in respiratory health through swimming can support overall lung function and promote better breathing patterns.
Boosts Heart Efficiency
Swimming laps regularly challenges your cardiovascular system, making your heart stronger and more efficient. Water resistance forces you to work harder with each stroke, which boosts your heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. As you refine your stroke technique, you optimize movement and reduce unnecessary effort, further enhancing heart efficiency. Proper form helps you use energy more efficiently, reducing fatigue and allowing you to sustain activity longer. Consistent swimming improves circulation and helps your heart adapt to increased demands. Additionally, practicing aerobic exercises can promote mental resilience and reduce stress, supporting overall heart health. Incorporating data-driven strategies, such as tracking your workout metrics, can help you optimize your training for maximum cardiovascular benefit.
Improves Lung Capacity
Engaging in regular lap swimming can considerably boost your lung capacity, which in turn enhances your overall cardiovascular endurance. As you swim, you develop better breath control, forcing you to manage your inhalations and exhalations more efficiently. This practice strengthens your respiratory muscles and improves your respiratory health, allowing you to take in more oxygen with each breath. Over time, your lungs become more elastic and efficient at exchanging gases, contributing to increased stamina. Enhanced lung capacity helps you sustain activity longer without feeling winded, making your workouts more effective. Consistent swimming also reduces respiratory issues, supporting long-term respiratory health. By focusing on controlled breathing during your swim sessions, you naturally foster stronger lungs and better cardiovascular performance.
Builds Endurance Over Time
Regularly practicing lap swimming gradually builds your endurance, allowing your heart and muscles to work more efficiently over time. As you swim, you develop better breath control, enabling you to sustain activity longer without fatigue. Improving your mental focus helps you maintain a steady pace and stay consistent during workouts. Over time, this combination enhances your cardiovascular endurance, making everyday activities easier. Consistent swimming also trains your body to recover quicker and handle increased exertion. To maximize these benefits, focus on:
- Maintaining steady breathing patterns
- Staying mentally engaged during laps
- Gradually increasing swim duration
- Practicing deliberate, controlled movements
Additionally, understanding the importance of diversify investments can help prevent overexertion and support your overall fitness goals. Incorporating proper training techniques ensures you build endurance safely and effectively. Paying attention to body recovery is essential for sustained progress and injury prevention. Engaging in proper nutrition and hydration supports your endurance training and recovery, optimizing your performance. With dedication, you’ll notice improved stamina and overall fitness, making swimming a powerful tool for building endurance over time.
Builds Lean Muscle Mass
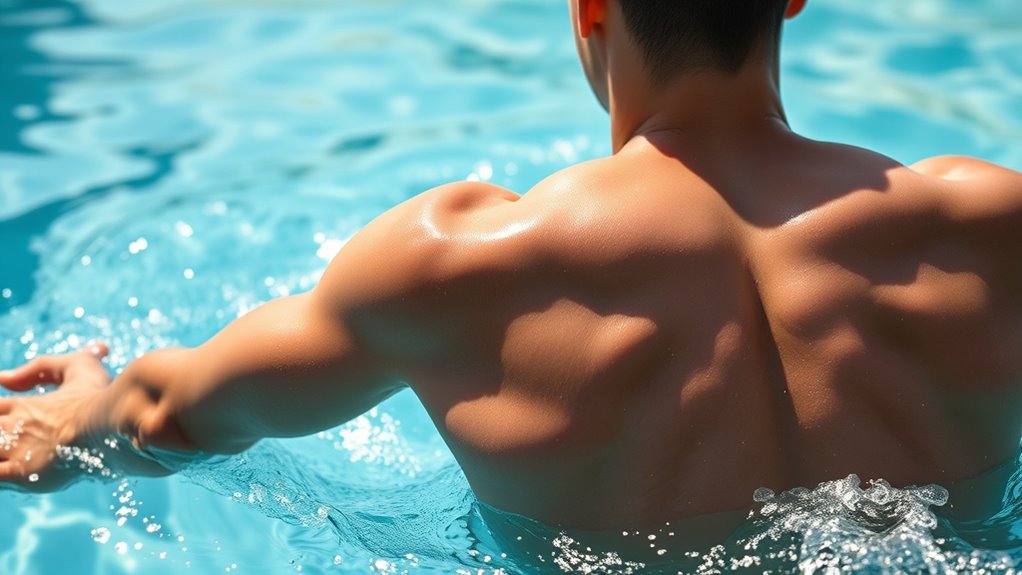

Because lap swimming involves resistance from the water, it effectively tones and builds lean muscle mass. The water’s natural resistance forces your muscles to work harder with each stroke, leading to increased muscle endurance over time. As you push through the water, your muscles adapt by becoming stronger and more defined, especially in your arms, shoulders, back, and core. Unlike some workouts that require weights or machines, swimming provides a full-body strength training session that’s gentle on your joints. The continuous resistance challenges your muscles consistently, helping you develop lean, toned muscles without bulk. Plus, the more you swim, the better your muscle endurance becomes, supporting overall strength and physical fitness.
Burns Calories Effectively

As your muscles become stronger and more defined through swimming, your body also burns calories more efficiently. The water temperature and pool environment play key roles in maximizing calorie burn. Cooler water forces your body to work harder to regulate temperature, increasing energy expenditure. Additionally, swimming against the current or performing interval training amps up calorie burning. The resistance of water makes every stroke more effective. To optimize results, consider:
- Swimming in slightly cooler water to boost calorie burn
- Using high-intensity intervals during your workout
- Incorporating varied strokes for full-body engagement
- Maintaining a consistent pace throughout your session
Improves Flexibility and Range of Motion

Swimming naturally stretches and mobilizes your muscles, leading to improved flexibility and a greater range of motion. As you glide through the water, your body performs stretching routines that target key muscle groups, helping to loosen tightness and increase elasticity. Incorporating flexibility exercises into your swimming routine enhances this benefit, making your muscles more adaptable and reducing the risk of injury. The resistance of water encourages gentle, sustained stretches, which improve joint mobility over time. Regular swimming sessions gradually loosen stiff muscles, allowing for smoother movements and better overall flexibility. By consistently engaging in stretching routines during your swim, you’ll notice increased ease in everyday activities and greater comfort in your body’s movements.
Boosts Core Strength and Stability

Engaging in lap swimming effectively builds your core strength and stability. The water’s buoyancy reduces impact, allowing you to focus on core engagement without strain. As you push against aquatic resistance, your abdominal, back, and oblique muscles work harder to stabilize your body. This continuous effort enhances your overall core power.
Swimming builds core strength, stability, and endurance through water resistance and buoyancy support.
- Water resistance challenges your muscles with every stroke
- Buoyancy supports proper posture and alignment
- Rotating your torso activates deep core muscles
- Consistent movement improves endurance and stability
Promotes Muscle Symmetry and Balance
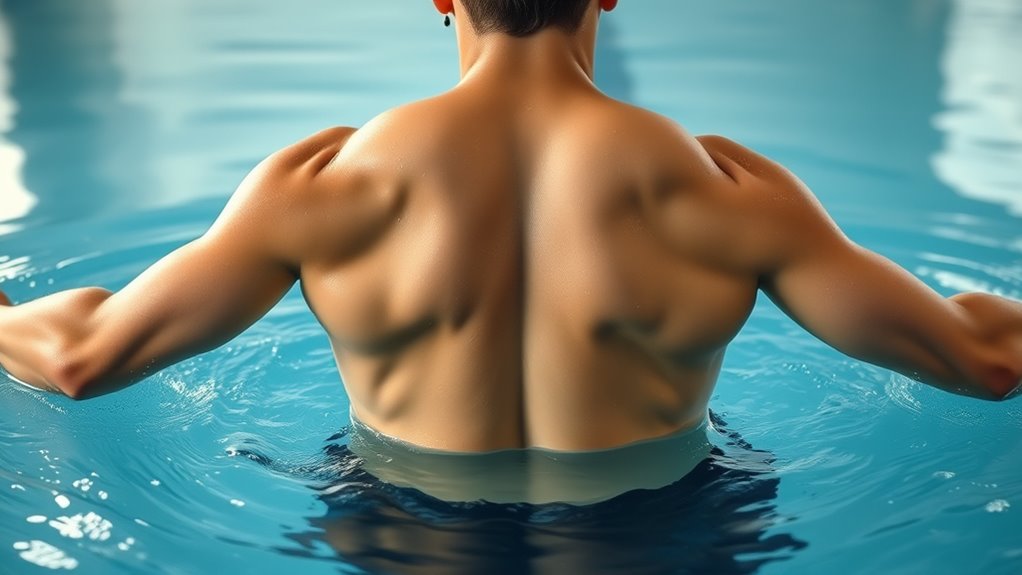
When you swim laps, you activate multiple muscle groups, helping to develop balanced strength throughout your body. This activity also encourages proper postural alignment, reducing the risk of muscle imbalances. As a result, your muscle development becomes more symmetrical, supporting overall stability and health.
Engages Multiple Muscle Groups
Because it requires coordinated movement of various muscle groups, lap swimming effectively promotes muscle symmetry and balance. Water resistance challenges your muscles evenly, ensuring that multiple groups work together efficiently. As you swim, your arms, legs, core, and back engage simultaneously, improving muscle coordination. This full-body workout helps prevent muscle imbalances, leading to a more harmonious physique.
- Enhances overall muscle engagement with minimal joint stress
- Strengthens both primary and stabilizer muscles
- Promotes even development across different muscle groups
- Supports functional movement and coordination
Encourages Postural Alignment
Swimming laps naturally encourages proper postural alignment by requiring you to maintain a streamlined position in the water. This constant focus enhances your postural awareness, helping you recognize and correct misalignments. As you swim, your muscles work together to keep your spine in neutral alignment, promoting spinal health and symmetry. Consistent practice balances muscle development, ensuring each side of your body supports your posture equally. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Benefits of Postural Alignment | How Swimming Helps |
|---|---|
| Improves spinal health | Maintains neutral spinal alignment during strokes |
| Enhances muscle symmetry | Engages opposing muscle groups evenly |
| Boosts postural awareness | Reinforces correct posture through mindful movement |
Balances Muscle Development
Maintaining proper postural alignment during lap swimming naturally promotes balanced muscle development across your body. When you swim with good posture, you engage muscles evenly, enhancing muscle symmetry and preventing imbalances. This balanced approach helps you develop a strong, coordinated physique while reducing injury risk. To maximize muscle symmetry, focus on core stability and proper technique, which ensure all muscle groups work harmoniously. Consistent swimming targets both sides of your body equally, fostering even muscle growth. Remember, maintaining postural alignment isn’t just about appearance—it supports functional strength and overall health. Incorporate drills that emphasize symmetry, such as single-arm strokes or focus on body position, to optimize muscle development and enjoy the full benefits of balanced toning.
Supports Weight Management Goals

Engaging in regular lap swimming can considerably support your weight management goals. Water’s hydrodynamic resistance makes every stroke a full-body workout, helping you burn calories efficiently. Unlike other forms of exercise, water provides natural resistance that challenges your muscles without excess impact, keeping your joints safe. Water buoyancy also plays a vital role by supporting your body and reducing strain, allowing you to stay active longer. This combination of resistance and buoyancy helps increase your metabolic rate, aiding fat loss and weight control. Plus, swimming is a sustainable activity you can enjoy regularly, making it easier to stick with your routine. By incorporating lap swimming into your schedule, you create an effective, low-impact way to reach and maintain your weight management goals.
Offers Customizable Workout Intensity

Lap swimming allows you to tailor your workout to match your fitness level and goals. You can modify the water temperature to make your swim more comfortable or challenging, depending on your preference. Varying your swimming strokes—such as freestyle, backstroke, or butterfly—helps target different muscle groups and intensities. You also control the pace and duration of each session, making it easy to increase or decrease workout intensity as needed.
Customize your swim by adjusting water temperature, strokes, pace, and duration to match your fitness goals.
- Adjust water temperature for comfort or challenge
- Switch between swimming strokes to vary intensity
- Increase pace for high-intensity workouts
- Extend or shorten swim durations based on goals
This flexibility ensures your workout remains effective and aligned with your progress, helping you stay motivated and avoid plateaus.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Lap Swimming Help With Injury Recovery?
Lap swimming can definitely aid injury rehab and joint healing. You move gently through the water, reducing stress on your joints and muscles, which helps prevent further injury. The low-impact nature allows you to stay active while recovering, promoting blood flow and flexibility. As you swim, you support your body’s healing process, making it easier to regain strength and range of motion without risking additional damage.
How Does Swimming Improve Mental Health and Reduce Stress?
You might think stress is just part of life, but swimming proves otherwise. Ironically, as you glide through the water, you engage in mindfulness practice, focusing on your breath and movement. This promotes relaxation and releases endorphins, natural mood lifters. Swimming becomes a powerful stress reduction technique, helping you clear your mind and improve mental health. It’s a soothing activity that transforms chaos into calm, one stroke at a time.
Is Lap Swimming Suitable for Seniors or People With Disabilities?
You’ll find lap swimming suitable if you’re a senior or have disabilities because water resistance makes movement easier and supports joint flexibility. It’s a low-impact exercise that reduces strain on your joints while still providing an effective workout. Swimming allows you to build strength and endurance safely, and you can adjust your pace and strokes to match your comfort level. Always check with your healthcare provider before starting, but it’s generally a gentle, beneficial activity.
What Equipment Is Essential for Effective Lap Swimming Workouts?
For effective lap swimming workouts, you’ll need essential equipment like swimming goggles to protect your eyes and improve visibility underwater. A kickboard is also crucial for building leg strength and focusing on your kick technique. These tools help you maximize your workout, stay comfortable, and stay safe. With the right gear, you can improve your form, increase endurance, and enjoy a more efficient and enjoyable swimming session.
How Often Should Beginners Swim to See Fitness Improvements?
You should aim to swim at least 3 times a week as a beginner to see fitness improvements. Consistent training frequency helps build endurance and strength. Make sure to track your progress by noting distances, times, or how you feel after each session. Adjust your routine gradually to avoid overtraining and stay motivated. With regular practice and progress tracking, you’ll notice steady gains in your fitness and swimming skills.
Conclusion
By swimming laps, you engage your entire body, protect your joints, boost your endurance, build lean muscle, burn calories, strengthen your core, promote balance, support weight goals, and customize your workouts. It’s a versatile, low-impact, effective way to get toned and stay healthy. So immerse yourself, embrace the challenge, and experience the many benefits swimming offers. Make it your go-to exercise for strength, stamina, and overall wellness—because when you swim, you truly transform.









